Nissan has announced it will launch ‘affordable’ on-board bi-directional charging on selected electric vehicles from 2026.
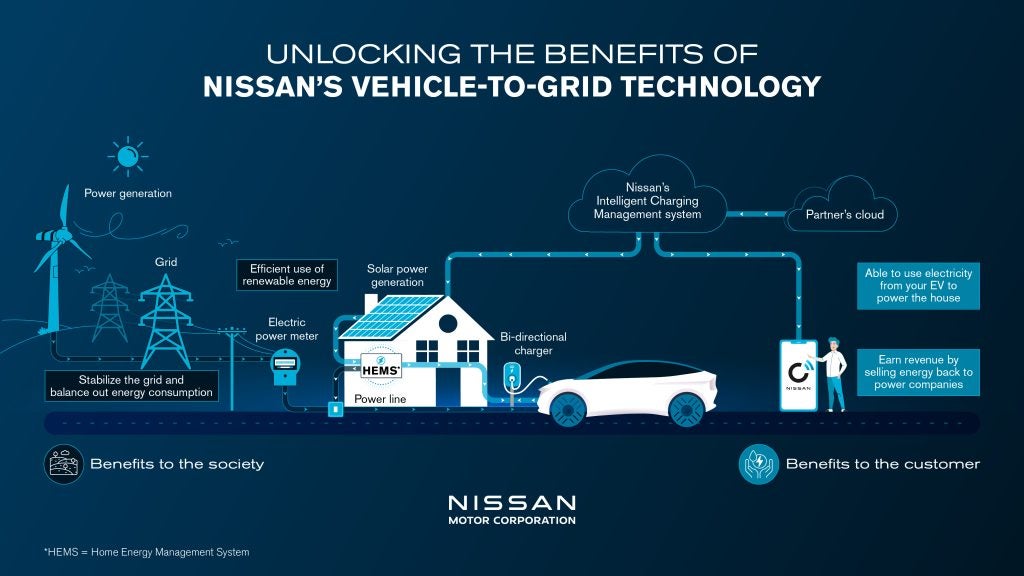
The Vehicle to Grid (V2G) technology, which allows EV owners to use electricity stored in their car’s battery to power their homes, or sell it back into the grid, will launch in the UK initially, followed by other markets in Europe.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
Nissan says the initiative forms a key step towards its vision of creating a sustainable energy ecosystem.
The project progresses the commitment made in Nissan’s business plan, The Arc, delivering differentiated innovation that enables the EV transition, while unlocking new revenue streams.
The project is underpinned by Nissan’s extensive experience in V2G, with around 40 pilot projects conducted worldwide throughout the past decade.
Following a successful year-long project at The University of Nottingham, UK, Nissan has become the first car company to gain G99 Grid code certification with an AC-based solution, needed to supply electricity into the UK national energy supply.
Under the banner of Nissan Energy, the company’s aim is to roll-out V2G technology across markets in Europe and beyond, empowering consumers with either AC or DC-based V2G solutions, in alignment with local infrastructure and regulatory requirements.
Benefits of V2G tech
Nissan says that by using Nissan’s on-board bi-directional V2G technology, customers can cut the annual cost of powering an EV by 50%. The same technology can also reduce net CO2 emissions from charging by 30% per year, per EV for the average UK household, the company maintains.
EVs equipped with V2G technology can play a crucial role in integrating and increasing the mix of renewables into the energy supply, by storing electricity generated by wind or solar, and directing it back into the grid when needed, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
As one of the bi-directional systems Nissan plans to offer, this AC-bidirectional system certified in the UK will leverage an integrated on-board charger to deliver a lower cost of entry, allowing the technology to be accessible to more people. Nissan aims to offer its AC bi-directional charger at a price comparable to a mono-directional charger available today.
As well as lowering the cost of entry, Nissan says its V2G system will give customers complete control and flexibility over their energy via a dedicated App.
Hugues Desmarchelier, Nissan Vice President, Global Electrification Ecosystem & EV Programs, said: “The technology we are bringing to customers is a potential game-changer for how we view the car. Not just as a means of getting from A to B, but as a mobile energy storage unit, capable of saving people money, supporting the transition of our energy systems away from fossil fuels and bringing us closer to a carbon-free future.
“Nissan is proud to democratise technology for the benefit of society. The breakthrough in an on-board solution for two-way charging will be a substantial reduction in the cost of integrating a future EV into your energy supply, and the ability to leverage the car as a source of income over its lifecycle.”
Successful UK trial
The V2G UK trial has been partly funded by the UK Government’s Advanced Propulsion Centre UK (APC), a body established to support and accelerate the automotive industry’s transition towards net zero.
APC Chief Executive, Ian Constance, said: “This is a significant milestone for the collaborative research and development project, led by Nissan Technical Centre Europe and supported by the Department for Business and Trade through the APC. Investing in pioneering vehicle-to-grid technology and R&D in the UK is part of a system-level approach to decarbonisation.”
Future of Roads Minister Lilian Greenwood, said: “Vehicle to grid technology is a fantastic innovation which has the potential to save people money and accelerate the UK’s transition to electric vehicles.
“A greener transport network is a key priority for this Government, and by working together with industry we will boost consumer confidence and achieve our shared goal of getting more EVs on the road.”
During the trial, Nissan worked with several partners including Dreev and Enovates.
Dreev, a joint venture between EDF and NUVVEF, was responsible for data collection, customer profiling and setting the charging and discharging plan by analysing information from the wall box.
Eric Mévellec, CEO for Dreev commented: “We have been working alongside Nissan for years on this revolutionary technological adventure, and we are thrilled to be a part of this new chapter. We are convinced that, by reducing the electricity bill for the customers while providing huge storage capabilities for the electrical system, V2x technology has a major role to play in the energy transition”
Enovates, a Belgian-based mobility technology company, developed the wall box, or Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), including set-up and test certification.
The wall box acts as the system hub, sending and receiving information on energy demand and supply from the Dreev cloud, and directing the car to charge or discharge electricity at a set amount to the home or grid.
Bart Vereecke, CEO of Enovates, said: “Enovates is proud to partner with Nissan in demonstrating through the Field Operating Test the real-world benefits of AC V2G technology. This test marks an important step in creating a sustainable, interconnected energy future where electric vehicles play a central role in sustainable mobility solutions and resolving energy grid congestions.”
“Enovates has always been committed to pushing the boundaries of V2G technology, and we are excited to bring our expertise in AC charging to this project,” added Stijn Vispoel, R&D Manager. “Our certified AC V2G chargers represent the next generation of energy technology, offering accessible, efficient, and smart solutions for the future of transportation and energy.”
The University of Nottingham was also pivotal in the trial, providing a base of operations at its on-campus Creative Energy Homes and supporting academic research.
Nissan is continuing to work with these, and other partners, to achieve the necessary grid certification in other markets, develop a seamless user experience and expand the technology availability to more customers.
Chairperson of Nissan’s Africa, Middle East, India, Europe and Oceania region, Guillaume Cartier, commented: “One of the big challenges faced by society today is energy supply – how do we make it affordable, reliable and clean.
“At Nissan, we see a future for our customers where their energy comes from the car on the driveway – not only the power station – fully integrated, flexible and cleaner.”